本文共 16463 字,大约阅读时间需要 54 分钟。
SpringBoot+MyBatis搭建迷你小程序
开发环境
- jdk:java version “1.8.0_152”
- Itell IDEA (可凭学生邮箱注册免费使用)
- maven3.3.9
- mysql-community-5.7.21
- sqlyog
步骤
1.项目新建及配置
JDK之类的配置就不多说了,新建项目;
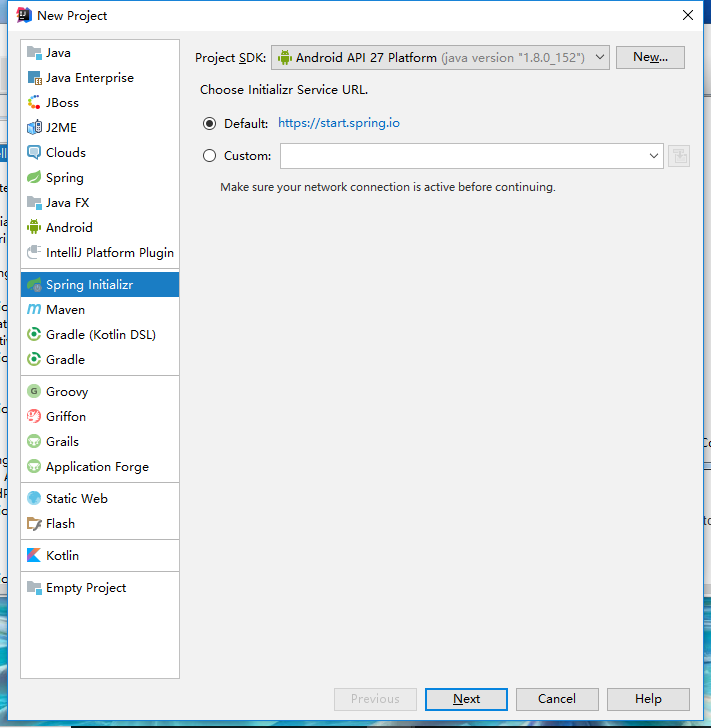 对了,当时不记得了,别勾选Android相关配置,不然后面会出问题的。 选中【Spring Initializr】,设置好【Project SDK】;
对了,当时不记得了,别勾选Android相关配置,不然后面会出问题的。 选中【Spring Initializr】,设置好【Project SDK】; 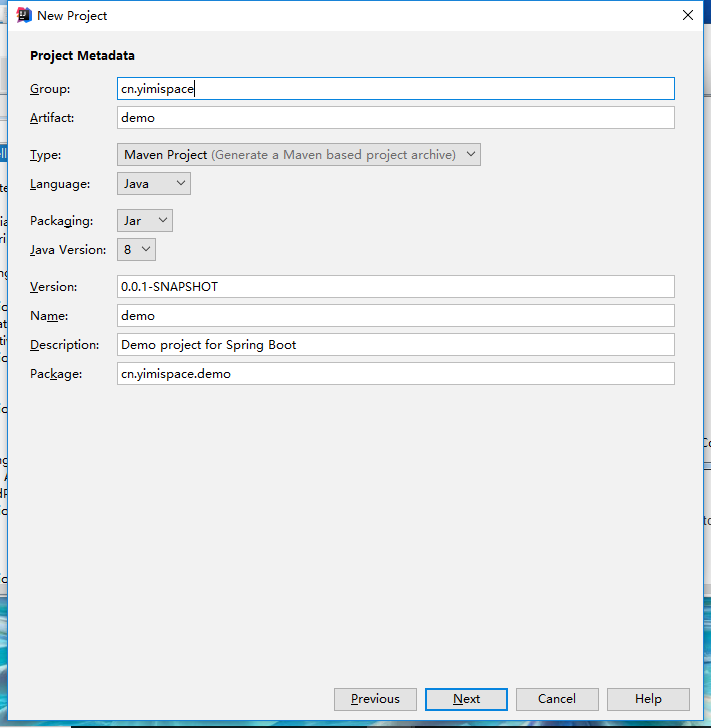
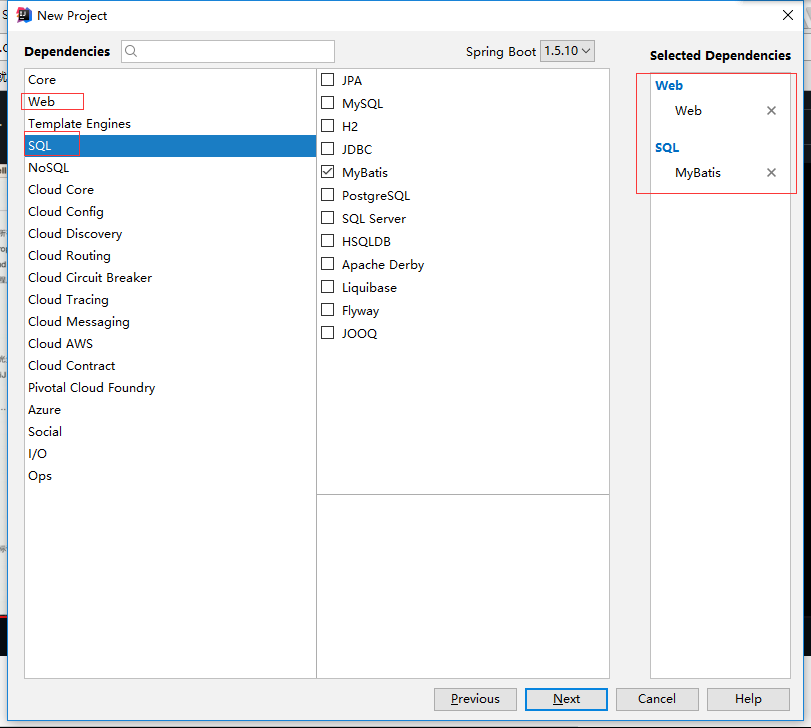 勾选Web下的web和SQL下的MyBatis,然后Next……Finish。
勾选Web下的web和SQL下的MyBatis,然后Next……Finish。 
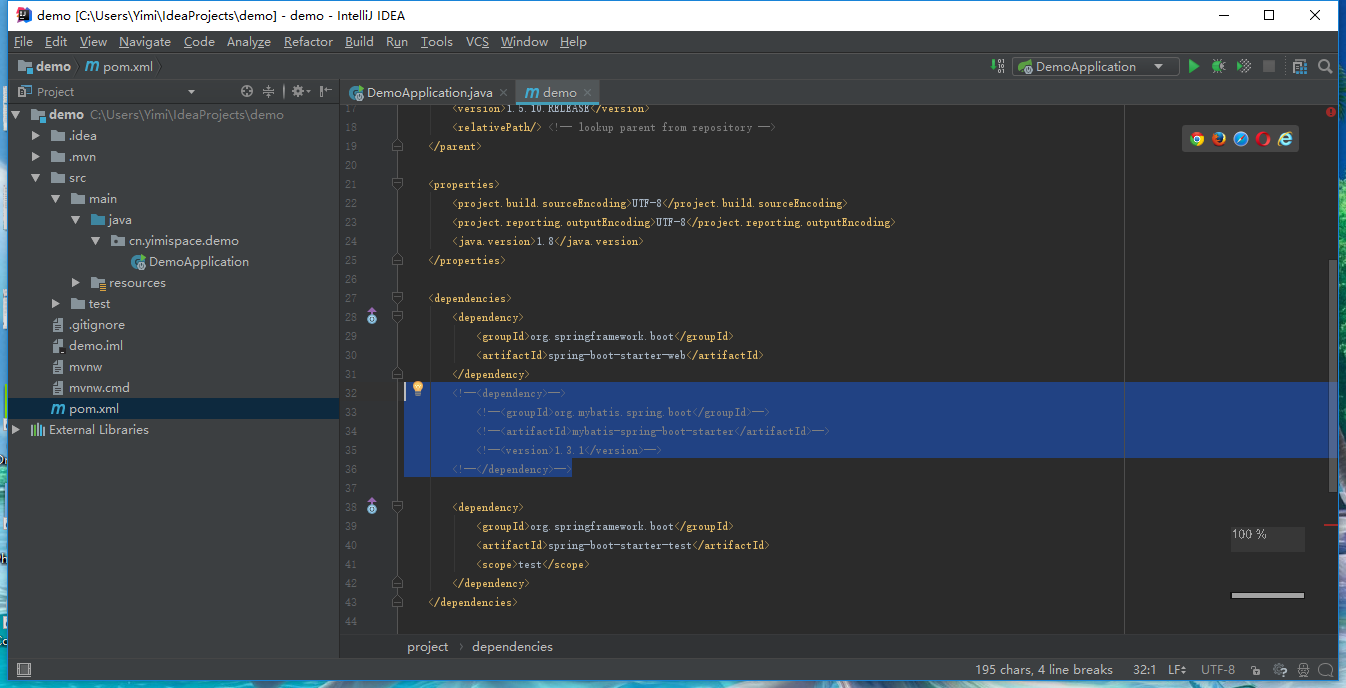 因为之前手动勾选设好了Maybatis的配置了,所以现在可以把pom.xml配置文件里的这段注释掉;
因为之前手动勾选设好了Maybatis的配置了,所以现在可以把pom.xml配置文件里的这段注释掉; org.mybatis.spring.boot mybatis-spring-boot-starter 1.3.1
然后记得点击右下角重新导入Maven依赖。

测试SpringBoot在Web端运行(只是测试,可跳过此步)
新建Hello类
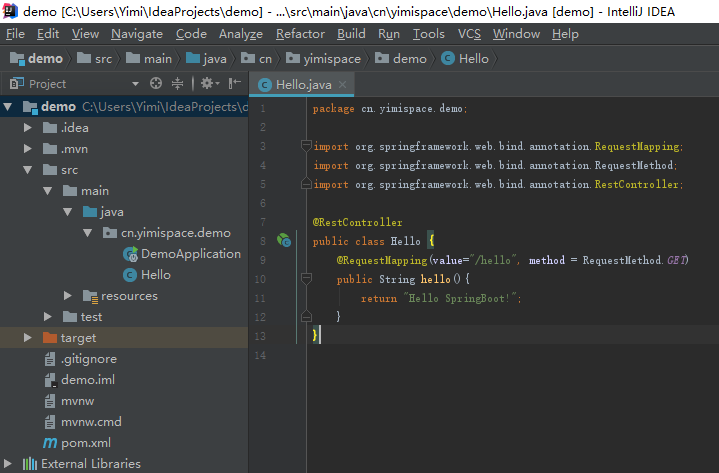 代码如下:
代码如下: package cn.yimispace.demo;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@RestControllerpublic class Hello { @RequestMapping(value="/hello", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String hello(){ return "Hello SpringBoot!"; }} 然后点击运行,在浏览器url处输入:
http://localhost:8080/
即可运行。
如果想换端口或者添加根路径也可在application.properties文件自己配置: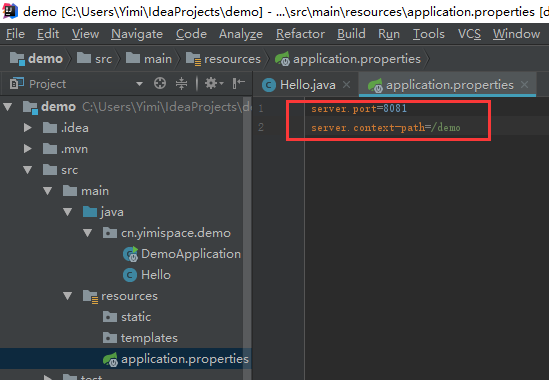 然后运行,Web显示如下:
然后运行,Web显示如下: 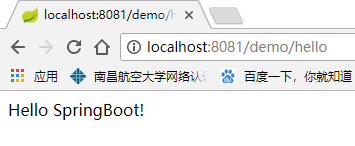
项目后台开发
1. 使用SQLyog创建数据库及表
数据库名:Yimi
表名:plan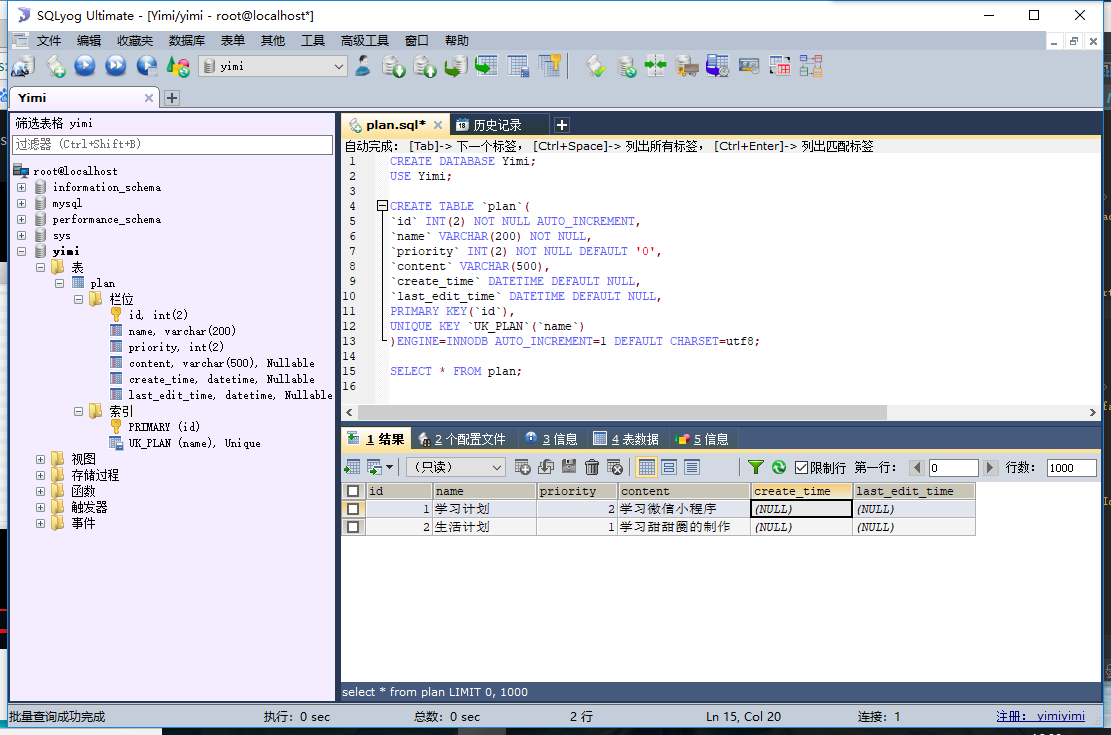
CREATE DATABASE Yimi;USE Yimi;CREATE TABLE `plan`(`id` INT(2) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`name` VARCHAR(200) NOT NULL,`priority` INT(2) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',`content` VARCHAR(500),`create_time` DATETIME DEFAULT NULL,`last_edit_time` DATETIME DEFAULT NULL,PRIMARY KEY(`id`),UNIQUE KEY `UK_PLAN`(`name`))ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;SELECT * FROM `plan`;
2. 修改pom.xml文件
打开IDEA的项目,修改pom.xml文件。
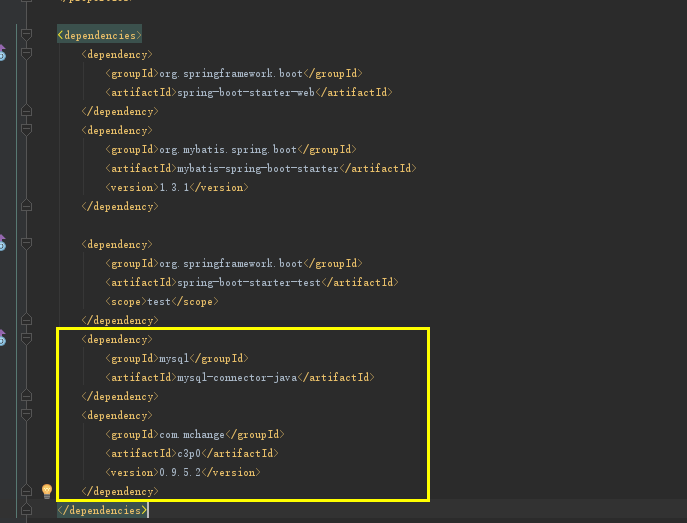 添加的代码如下:
添加的代码如下: mysql mysql-connector-java com.mchange c3p0 0.9.5.2
3.新建entity包,在此包内新建Plan类
表中字段与此类一一对应,并添加相应getter,setter方法。
package cn.yimispace.demo.entity;import java.util.Date;public class Plan { private Integer id; //计划ID private String name; //计划名称 private Integer priority; //权重,越大越靠前显示 private String content; //内容 private Date createTime; //创建时间 private Date lastEditTime; //更新时间 public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } //...... 4.配置mybatis-config.xml
5.配置application.properties
用于连接数据库及地址映射相关操作。
server.port=8081server.context-path=/demo#DataSourceConfigurationjdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driverjdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yimi?useUnicode=true&useSSL=falsejdbc.username=rootjdbc.password=wanxinyan#SessionFactoryConfigurationmybatis_config_file=mybatis-config.xmlmapper_path=/mapper/**.xmlentity_package=cn.yimispace.demo.entity
6.DataSource配置
新建cn.yimispace.demo.config包,在此包下新建类DataSourceConfiguration,代码如下:
package cn.yimispace.demo.config;import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource;import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import java.beans.PropertyVetoException;/** * @Configuration 告诉Spring容器调用此类注入 * @MapperScan 配置mybatis mapper的扫描路径 */@Configuration@MapperScan("cn.yimispace.demo.dao")public class DataSourceConfiguration { @Value("${jdbc.driver}") private String driver; @Value("${jdbc.url}") private String url; @Value("${jdbc.username}") private String username; @Value("${jdbc.password}") private String password; /** * 设置连接池 * @return */ @Bean(name="dataSource") public ComboPooledDataSource createDataSource() throws PropertyVetoException { //普通java项目里不能导入安卓的包,否则会报Runningtime错及找不到PropertyVetoException ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource(); dataSource.setDriverClass(driver); dataSource.setJdbcUrl(url); dataSource.setUser(username); dataSource.setPassword(password); //关闭连接后不自动提交 dataSource.setAutoCommitOnClose(false); return dataSource; }} 7.SessionFactory配置
在cn.yimispace.demo.config包下新建SessionFactoryConfiguration类,代码如下:
package cn.yimispace.demo.config;import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;import javax.sql.DataSource;import java.io.IOException;@Configurationpublic class SessionFactoryConfiguration { @Value("${mybatis_config_file}") private String mybatisConfigFilePath; @Value("${mapper_path}") private String mapperPath; @Value("${entity_package}") private String entityPackage; @Autowired @Qualifier("dataSource") private DataSource dateSource; @Bean(name="sqlSessionFactory") public SqlSessionFactoryBean createSqlSessionFactoryBean() throws IOException { SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean(); sqlSessionFactoryBean.setConfigLocation(new ClassPathResource(mybatisConfigFilePath)); PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver resolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(); String packageSearchPath = PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver.CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX + mapperPath; sqlSessionFactoryBean.setMapperLocations(resolver.getResources(packageSearchPath)); sqlSessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(dateSource); sqlSessionFactoryBean.setTypeAliasesPackage(entityPackage); return sqlSessionFactoryBean; }} 8.DAO层
新建cn.yimispace.demo.dao包,在此包下新建接口PlanDao,代码如下:
package cn.yimispace.demo.dao;import cn.yimispace.demo.entity.Plan;import java.util.List;public interface PlanDao { //alt+enter键create test可创建测试单元 /** * 列出计划列表 * @return planList */ List queryPlan(); /** * 根据ID列出具体计划 * @param id * @return plan */ Plan queryPlanById(int id); /** * 插入计划信息 * @param plan * @return */ int insertPlan(Plan plan); /** * 更新计划信息 * @param plan * @return */ int updatePlan(Plan plan); /** * 删除计划信息 * @param id * @return */ int deletePlan(int id);} 要想DAO层能访问数据库内容,需要做映射,在resources目录下新建mapper文件夹,内新建PlanDao.xml,用于设置SQL代码,其中标签内配置的id等信息与类内方法一一对应,内容如下:
INSERT INTO PLAN(name,priority,content,create_time,last_edit_time) VALUES (#{name},#{priority},#{content},#{createTime},#{lastEditTime}) UPDATE plan WHERE id=#{id} name=#{name}, priority=#{priority}, content=#{content}, last_edit_time=#{lastEditTime}, DELETE FROM plan WHERE id=#{id}
接下来,可以对所写的DAO层方法进行测试,回到接口PlanDao的名字处使用alt+enter键create test可创建测试单元,在test文件夹下会自动生成cn.yimispace.demo.dao.PlanDaoTest类,然后对每个方法进行单元测试,暂时不测试的类可先写上@Ignore,形如以下代码:
package cn.yimispace.demo.dao;import cn.yimispace.demo.entity.Plan;import org.junit.Ignore;import org.junit.Test;import org.junit.runner.RunWith;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;import java.util.Date;import java.util.List;import static org.junit.Assert.*;@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)@SpringBootTestpublic class PlanDaoTest { @Autowired //Spring通过Autowire用于动态注入 private PlanDao planDao; @Test@Ignore public void queryPlan() { List planList = planDao.queryPlan(); //expected:2表示期望返回的结果条数 assertEquals(2, planList.size()); } @Test@Ignore public void queryPlanById() { Plan plan = planDao.queryPlanById(2); assertEquals("生活计划", plan.getName()); } @Test@Ignore public void insertPlan() { Plan plan = new Plan(); plan.setName("运动计划"); plan.setPriority(1); plan.setContent("跑一次全程马拉松"); int effectedNum = planDao.insertPlan(plan); assertEquals(1, effectedNum); } @Test@Ignore public void updatePlan() { Plan plan = new Plan(); plan.setContent("周游世界"); plan.setId(3); plan.setLastEditTime(new Date()); int effectedNum = planDao.updatePlan(plan); assertEquals(1,effectedNum); } @Test public void deletePlan() { int effectedNum = planDao.deletePlan(3); assertEquals(1,effectedNum); }} 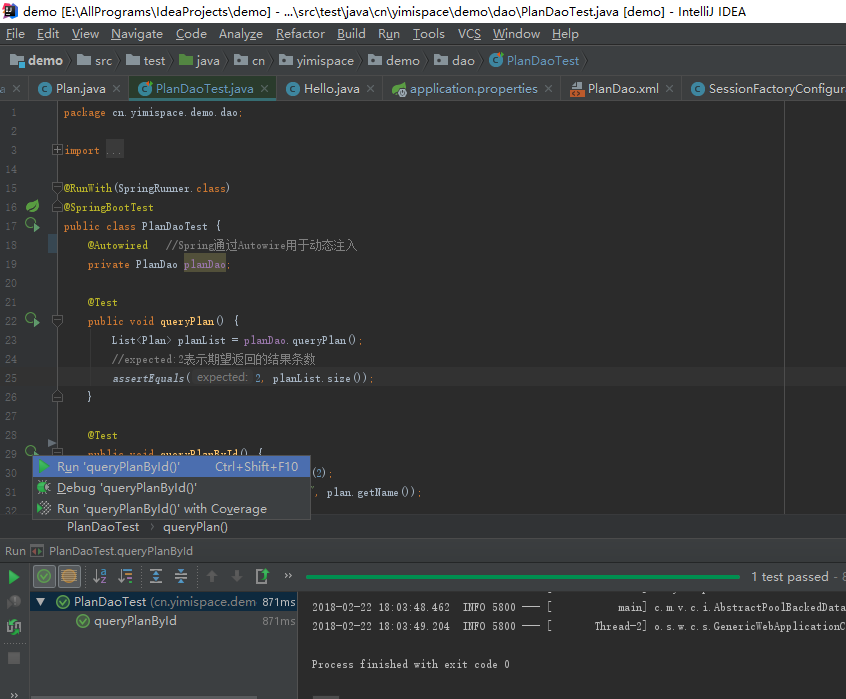
9.Service层
新建cn.yimispace.demo.service.PlanService接口:
package cn.yimispace.demo.service;import cn.yimispace.demo.entity.Plan;import java.util.List;public interface PlanService { /** * 列出计划列表 * @return planList */ List getPlanList(); /** * 根据ID列出具体计划 * @param id * @return plan */ Plan queryPlanById(int id); /** * 添加计划信息 * @param plan * @return */ boolean addPlan(Plan plan); /** * 修改计划信息 * @param plan * @return */ boolean modifyPlan(Plan plan); /** * 删除计划信息 * @param id * @return */ boolean deletePlan(int id);} 新建cn.yimispace.demo.service.impl.PlanServiceImpl类实现接口:
package cn.yimispace.demo.service.impl;import cn.yimispace.demo.dao.PlanDao;import cn.yimispace.demo.entity.Plan;import cn.yimispace.demo.service.PlanService;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;import java.util.Date;import java.util.List;@Servicepublic class PlanServiceImpl implements PlanService { @Autowired private PlanDao planDao; /** * 列出计划列表 * * @return planList */ @Override public List getPlanList() { return planDao.queryPlan(); } /** * 根据ID列出具体计划 * * @param id * @return plan */ @Override public Plan queryPlanById(int id) { return planDao.queryPlanById(id); } /** * 添加计划信息 *@Transactional * 默认回滚RuntimeException类型的异常, * 若想回滚所有Exception异常可改为@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class) * @param plan * @return */ @Transactional @Override public boolean addPlan(Plan plan) { if(plan.getName() != null && !"".equals(plan.getName())){ plan.setCreateTime(new Date()); plan.setLastEditTime(new Date()); try{ int effectedNum = planDao.insertPlan(plan); if(effectedNum > 0){ return true; }else{ throw new RuntimeException("插入计划信息失败!"); } }catch(Exception e){ throw new RuntimeException("插入计划信息失败:" + e.getMessage()); } }else{ throw new RuntimeException("计划信息不能为空!"); } } /** * 修改计划信息 * * @param plan * @return */ @Override public boolean modifyPlan(Plan plan) { if(plan.getId() != null && plan.getId() > 0){ plan.setLastEditTime(new Date()); try{ int effectedNum = planDao.updatePlan(plan); if(effectedNum > 0){ return true; }else{ throw new RuntimeException("更新计划信息失败!"); } }catch(Exception e){ throw new RuntimeException("更新计划信息失败:" + e.toString()); } }else{ throw new RuntimeException("计划信息不能为空!"); } } /** * 删除计划信息 * * @param id * @return */ @Override public boolean deletePlan(int id) { if(id > 0){ try{ int effectedNum = planDao.deletePlan(id); if(effectedNum > 0){ return true; }else{ throw new RuntimeException("删除计划信息失败!"); } }catch(Exception e){ throw new RuntimeException("删除计划信息失败:" + e.toString()); } }else{ throw new RuntimeException("计划id不能为空!"); } }} 当然,写好后也可以仿照之前介绍的方法进行单元测试,效果如图:
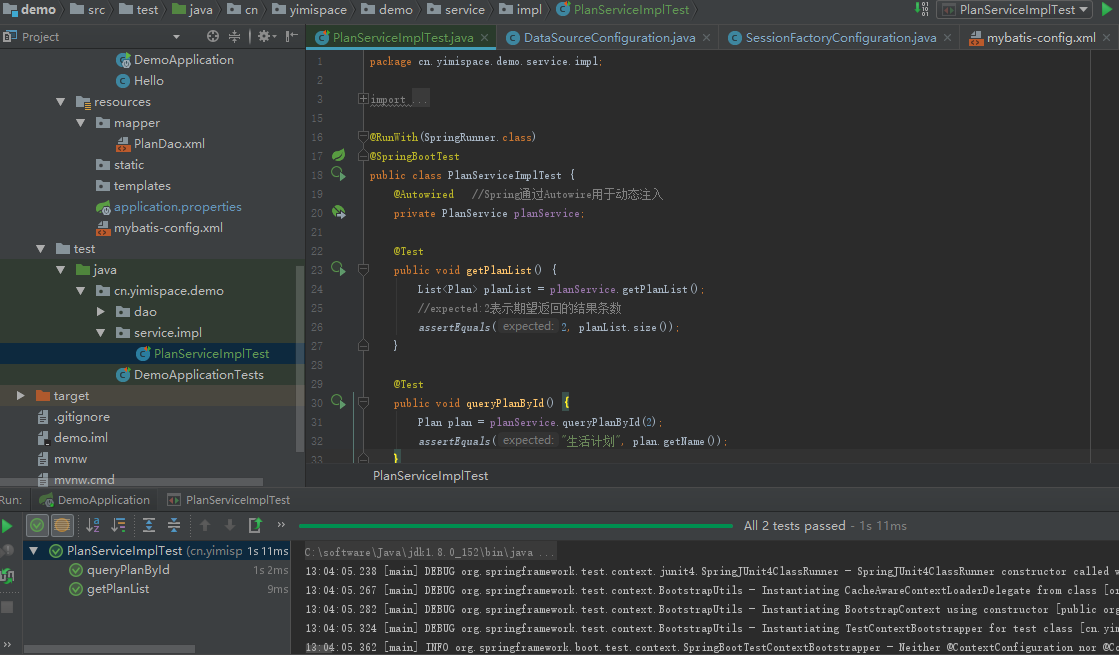
10.业务Controller方法实现
新建cn.yimispace.demo.web.PlanController类:
package cn.yimispace.demo.web;import cn.yimispace.demo.entity.Plan;import cn.yimispace.demo.service.PlanService;import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonParseException;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonMappingException;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;import java.io.IOException;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.List;import java.util.Map;/** * @RestController * 即@ResponseBody与@Controller的组合 * 因为返回的不是页面,而是body值 * @RequestMapping("/superadmin") * 设置根路由(最好小写) */@RestController@RequestMapping("/superadmin")public class PlanController { @Autowired private PlanService planService; /** * 启动DemoApplication在浏览器访问 * http://localhost:8081/demo/superadmin/listplan * 即可查到返回的内容 * @return */ @RequestMapping(value = "/listplan", method = RequestMethod.GET) private Map listPlan(){ Map modelMap = new HashMap (); List list = planService.getPlanList(); modelMap.put("planList", list); return modelMap; } @RequestMapping(value="/getplanbyid", method = RequestMethod.GET) private Map getPlanById(Integer id){ Map modelMap = new HashMap (); Plan plan = planService.queryPlanById(id); modelMap.put("plan", plan); return modelMap; } /** * @RequestBody 使前端传参以对象方式获取plan到后台 * @param plan * @return */ @RequestMapping(value="/addplan", method = RequestMethod.POST) private Map addPlan(@RequestBody Plan plan){ Map modelMap = new HashMap (); modelMap.put("success", planService.addPlan(plan)); return modelMap; } @RequestMapping(value="/modifyplan", method = RequestMethod.POST) private Map modifyPlan(@RequestBody Plan plan){ Map modelMap = new HashMap (); modelMap.put("success", planService.modifyPlan(plan)); return modelMap; } @RequestMapping(value="/removeplan", method = RequestMethod.GET) private Map removePlan(@RequestBody Integer id){ Map modelMap = new HashMap (); modelMap.put("success", planService.deletePlan(id)); return modelMap; }} 11.异常处理类
新建cn.yimispace.demo.handle.GlobalExceptionHandle用于处理DAO,Service,Controller等抛出的异常。
package cn.yimispace.demo.handle;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;/** * 异常处理类: * 用于处理DAO,Service,Controller等抛出的异常 */@ControllerAdvicepublic class GlobalExceptionHandle { /** * @ExceptionHandler(value=Exception.class) * 也可自定义错误类,抛出异常时new处自定义的错误类进行处理 * @param req * @param e * @return */ @ExceptionHandler(value=Exception.class) @ResponseBody private Map exceptionHandler(HttpServletRequest req, Exception e){ Map modelMap = new HashMap (); modelMap.put("success", false); modelMap.put("errMsg", e.getMessage()); return modelMap; }} 若抛出了异常可根据Json键值对"success"为false及"errorMsg"显示错误信息,可以测试一下此类是否生效。例如:可在PlanController类的listPlan()方法中写int x = 1/0;运行DemoApplication,则Web端显示Json报错信息。
报错情况: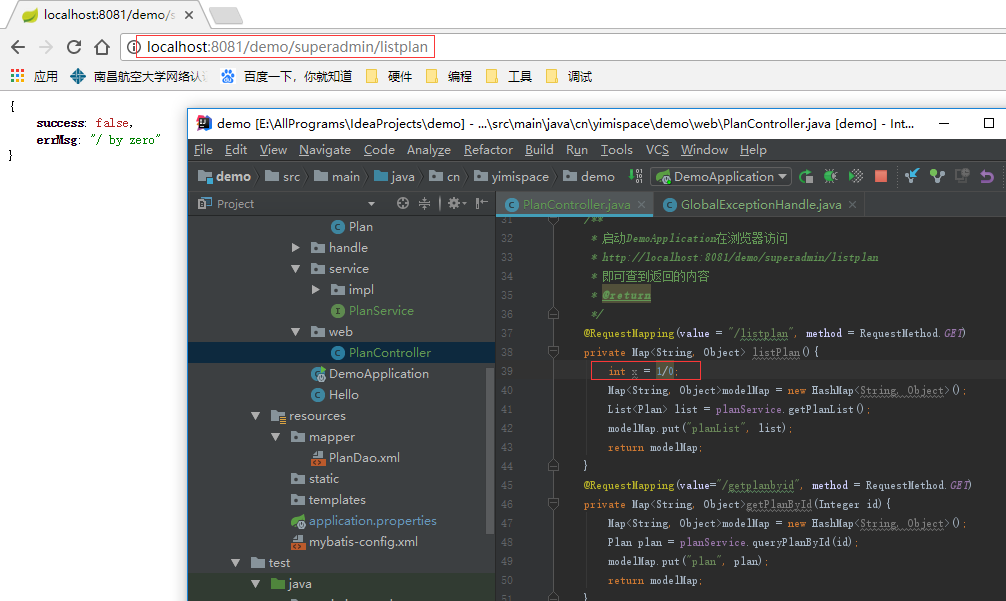 正常情况:
正常情况: 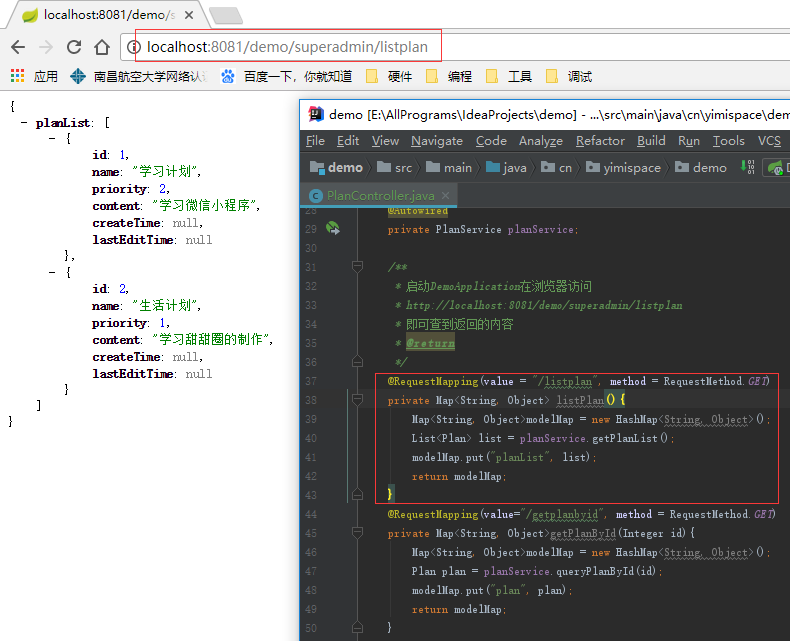
项目前端开发
1.工具准备及项目新建
微信小程序使用微信提供的开发工具,具体介绍可参见。
下载 用自己的微信扫码登录,在一个空文件夹里新建快速启动项目,打开效果如下: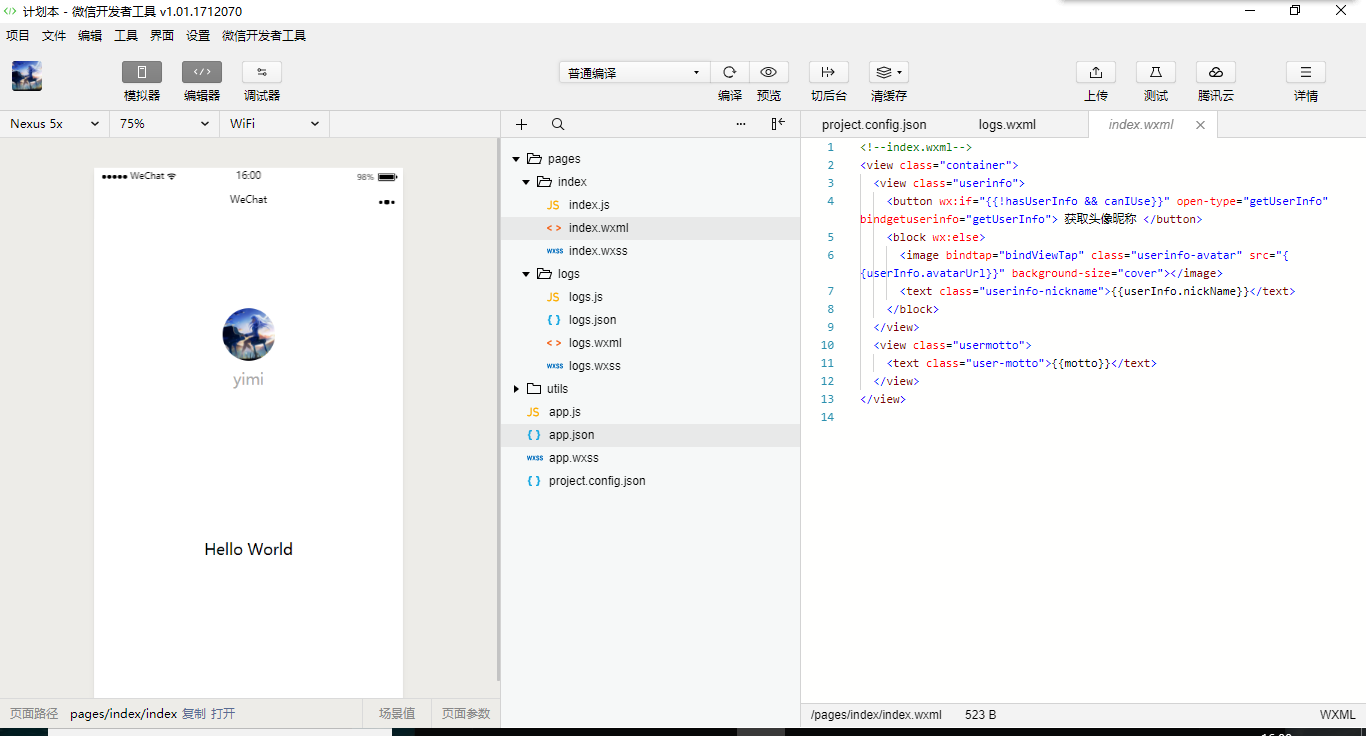
2.前端代码编写
在pages下新建list目录,在此目录下新建名为list的Page,微信开发者工具会自动生成相应的js,json,wxml,wxss文件,修改list.json文件用于改变计划列表页面标题栏:
{ "navigationBarTitleText": "计划信息列表"} 报错修改
使用IDEA写Autowired报错时,可做如下操作来解除报错
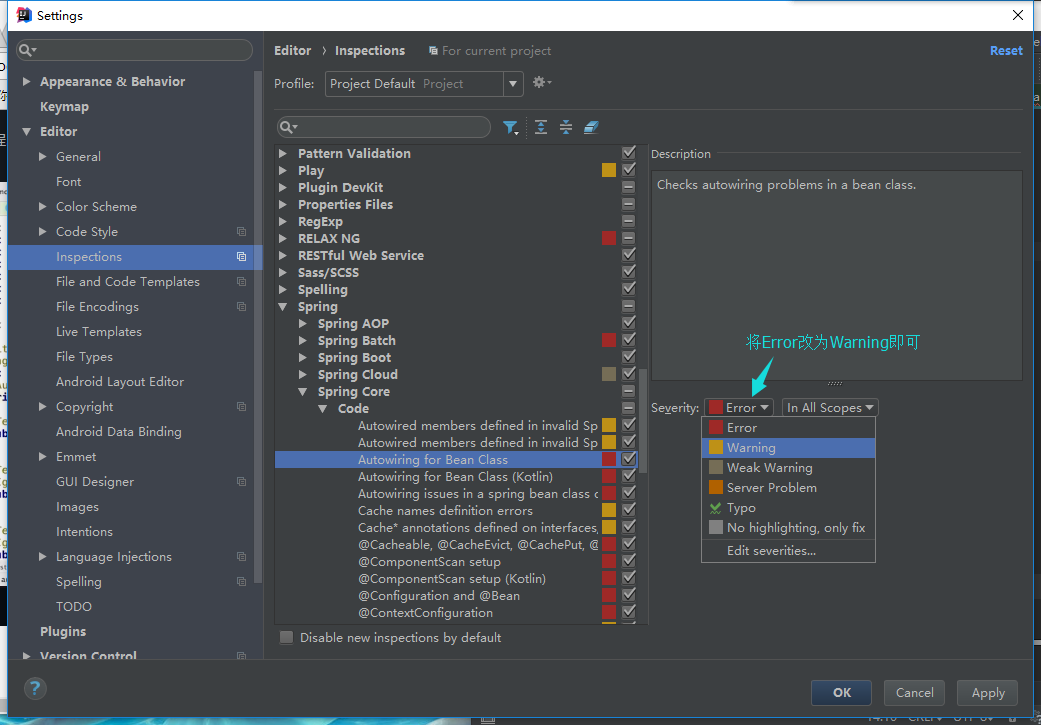
转载地址:http://wowmz.baihongyu.com/